What is Wi-Fi 7?
What is Wi-Fi 7?
Introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance, Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) is the latest standard in Wi-Fi technology, succeeding Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E. Wi-Fi 7 employs a variety of new technologies and protocols to reduce latency, increase network capacity, and boost efficiency. It delivers up to 100% faster connections and significantly better user experiences for client connects in high-density environments, and for video streaming and artificial reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences.
The key features of Wi-Fi 7 deliver higher data throughput and support deterministic latency for sophisticated use cases that demand first-rate reliability. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 7™ includes the following new features:
- 320 MHz super wide channels are only available in 6 GHz and provide twice the throughput of Wi-Fi 6, enabling multigigabit Wi-Fi device speeds
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO) supports more efficient load balancing of traffic among links, resulting in increased throughput and enhanced reliability
- 4K QAM achieves 20% higher transmission rates than Wi-Fi 6’s 1024 QAM for greater efficiency
- 512 Compressed Block Ack improves efficiency and reduces overhead
- Multiple RUs to a single STA improves flexibility for spectrum resource scheduling to enhance spectrum efficiency
These benefits are only available to Wi-Fi 7 client devices. Based on our experience through many generations of Wi-Fi innovations, we estimate that widespread adoption will gain momentum by 2026 , however, it is important to begin preparations now as early releases for Wi-Fi 7 supported devices are anticipated in fall 2024.
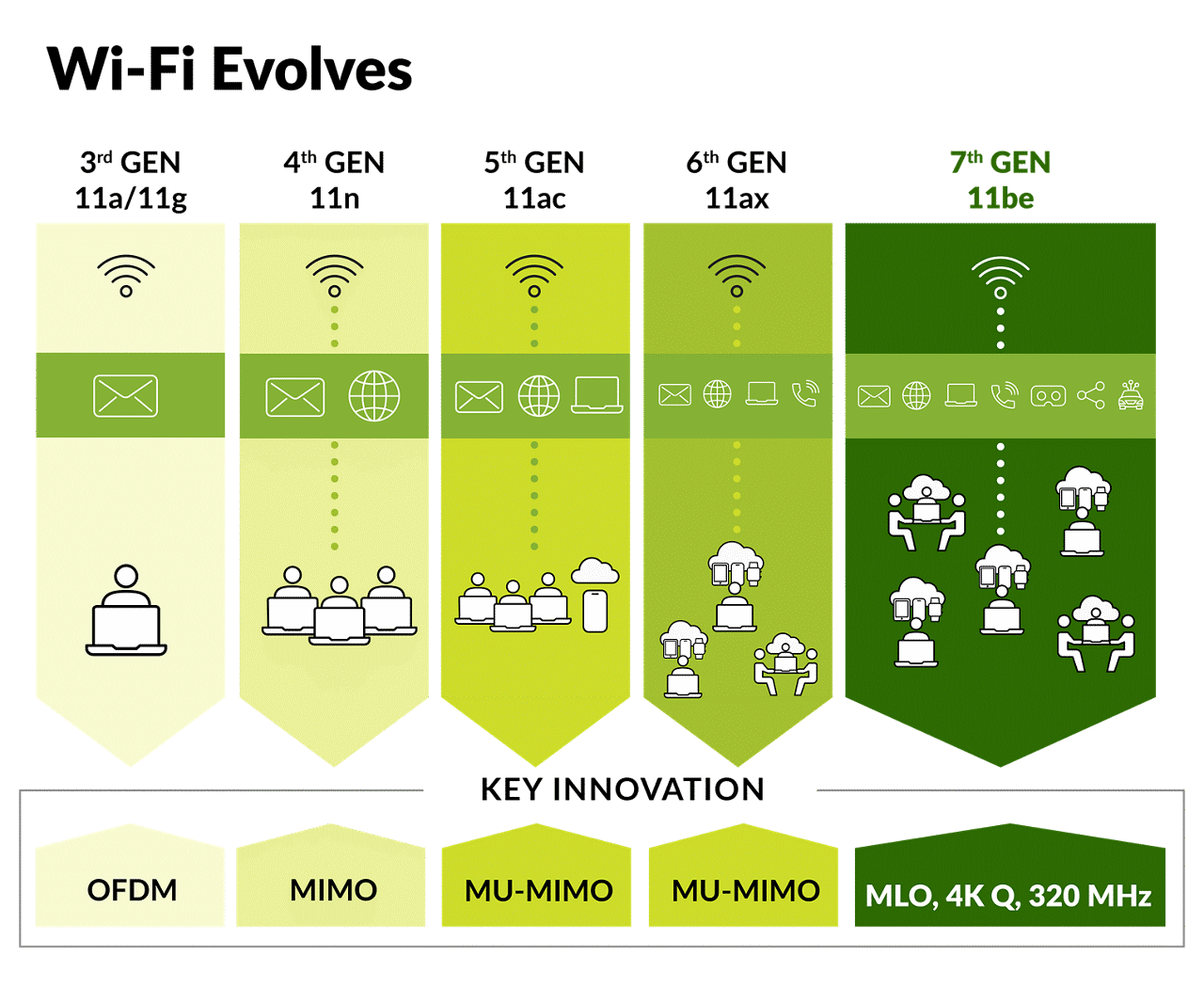
Figure 1. Wi-Fi 7 redefines connectivity with higher throughput, reduced latency, and extended range. It provides unmatched reliability for evolving digital demands.
What problem does Wi-Fi 7 solve?
Wi-Fi 7 addresses the growing demand for higher data throughput and improved reliability in increasingly connected environments. As a direct response to complex and high-density use cases, its design overcomes several prevalent challenges of previous Wi-Fi generations.
The standard introduces 320 MHz super wide channels, which are exclusive to the 6 GHz band, doubling the throughput of Wi-Fi 6. This feature, which is pivotal for handling multigigabit speeds required by bandwidth-intensive applications, provides a solution to the current congestion in traditional Wi-Fi bands.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO) further elevates the Wi-Fi experience by enhancing load balancing across links. The result is a significant increase in throughput and a leap in reliability, squarely addressing erratic performance due to imbalanced network loads—a critical issue in existing configurations.
Moreover, the leap from 1024 QAM to 4K QAM facilitates 20% higher transmission rates, pushing the efficiency envelope. Along with 512 Compressed Block Ack and the ability for Multiple Resource Units (RUs) to a single Station (STA), Wi-Fi 7 guarantees a transformative boost in spectrum efficiency and reduced overhead.
Collectively, Wi-Fi 7 innovations provide the backbone for networks capable of facilitating immersive experiences, such as AR/VR, without previous latency and inefficiency burdens.
As with every new generation of Wi-Fi, transitioning to Wi-Fi 7 will require systematic planning. Especially given its need for increased power, ongoing management considerations, and the expanded attack surface introduced by more and faster devices. Legacy devices must evolve to match Wi-Fi 7's sophistication, and the ecosystem will need time to mature.
How does Wi-Fi 7 work?
Wi-Fi 7, or IEEE 802.11be, represents the next evolution in wireless networking technology, building on the substantial advancements introduced with Wi-Fi 6 and the expansion into the 6 GHz spectrum by Wi-Fi 6E. Wi-Fi 7 promises to redefine user experiences in high-density environments like large campuses, stadiums, airports, and conference centers and support bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming video and AR and VR.
Wi-Fi 7 enhances connectivity by integrating several innovative features that push the boundaries of wireless technology:
- 320 MHz Channels: Exclusive to the 6 GHz band, these channels effectively double the throughput capabilities compared to Wi-Fi 6. This enhancement facilitates multi-gigabit speeds, propelling the performance of Wi-Fi networks to new heights.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): MLO is a pivotal feature that allows devices to utilize multiple Wi-Fi bands simultaneously. This not only boosts throughput by distributing traffic more efficiently but also enhances reliability and decreases latency, critical for applications requiring consistent and robust connectivity.
- 4K QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation): Wi-Fi 7 will leverage 4K QAM to deliver a 20% increase in transmission rates over 1024 QAM in Wi-Fi 6. This higher modulation scheme propels data throughput, achieving greater efficiency over the airwaves.
- 512 Compressed Block Acknowledgment BlockAck): This feature reduces overhead and boosts efficiency by efficiently handling acknowledgments, supporting higher data rates and improving overall network performance.
- Multiple Resource Units (MRU) allocation: Enhanced flexibility in spectrum resource scheduling is another significant advancement, allowing for better spectrum efficiency critical in dense network environments.
Strategic deployment considerations
Before jumping into deployment, enterprises should consider the following:
- Infrastructure readiness: Transitioning to a cloud-based network architecture integrated with native Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) is crucial. Harnessing the full potential of Wi-Fi 7 will require a modern network that can dynamically adapt to increased clients and data flows , simplify complex operations and manage heightened demands seamlessly.
- Access point power requirements: To fully leverage features like 320 MHz channels and 4K QAM, Wi-Fi 7 access points (APs) use significantly higher power than APs from previous generations. For applications in smart buildings, efficient power use extends beyond devices. Integrating power through switches aids in the sustainable deployment and management of smart technologies, such as smart lighting, by directly supplying power without overburdening the building's electrical systems.
- Device ecosystem: Adoption rates for Wi-Fi 7 technologies will start to accelerate in 2025, with widespread adoption expected by 2026. In the meantime, enterprises need to consider that Wi-Fi 7 will bring a dramatic increase in the number and types of connected devices and an expanded attack surface. Going forward, modern and robust Network Access Control (NAC) will be critical to closing gaps in the security posture. By performing checks and validations on devices before allowing them to access the network, NAC solutions enforce Zero Trust security policies.
- For near term deployments enterprises should initially focus on leveraging Wi-Fi 6E, which shares some underpinnings with Wi-Fi 7, particularly in operating within the 6 GHz spectrum.
Networking companies like Juniper offer products like the Wi-fi 6E ready Juniper AP45, AP34, AP24, and indoor/outdoor AP64, as well as the new Wi-Fi 7 ready AP47, that are paving the way for these transformations.Wi-fi 6E and 7 APs integrate advanced features that cater to the heightened requirements of the 6 GHz spectrum and beyond. Juniper’s focus on AI and automation also underscores the approach needed to simplify networking operations and control costs.
Looking ahead
With its unprecedented data speeds and ability to handle the demands of next-generation applications and support an ever-increasing number of wireless devices, Wi-Fi 7 will be a cornerstone of future-proof enterprise networks. Enterprises need to prepare for the advances by modernizing their architectures and adapting their operational strategies.
Networking companies like Juniper offer products like the Juniper AP45, AP34, AP24, and indoor/outdoor AP64, as well as the new Wi-Fi 7 ready AP47, that are paving the way for these transformations, integrating advanced features that cater to the heightened requirements of the 6 GHz spectrum and beyond. Their focus on AI and automation underscores the approach needed to simplify networking operations and control costs.
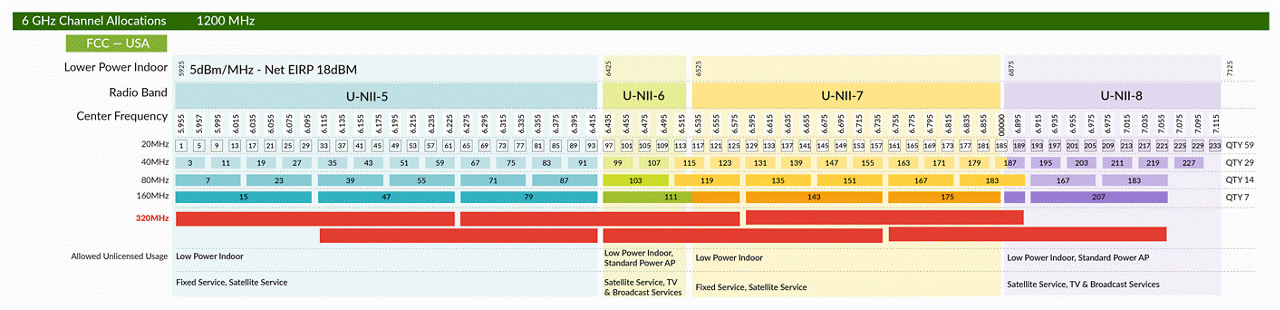
Figure 2. Experience doubled throughput with Wi-Fi 7's 320 MHz channels, enabling multi-gigabit speeds exclusively in the 6 GHz band.
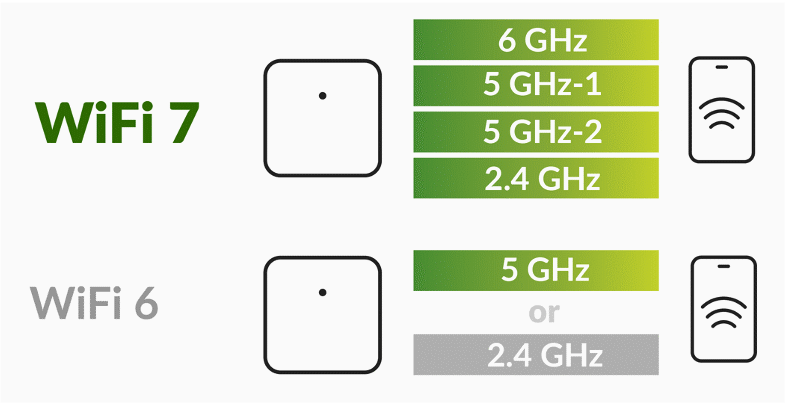
Figure 3. MLO: Elevating Wi-Fi efficiency and reliability with intelligent load balancing for superior throughput.
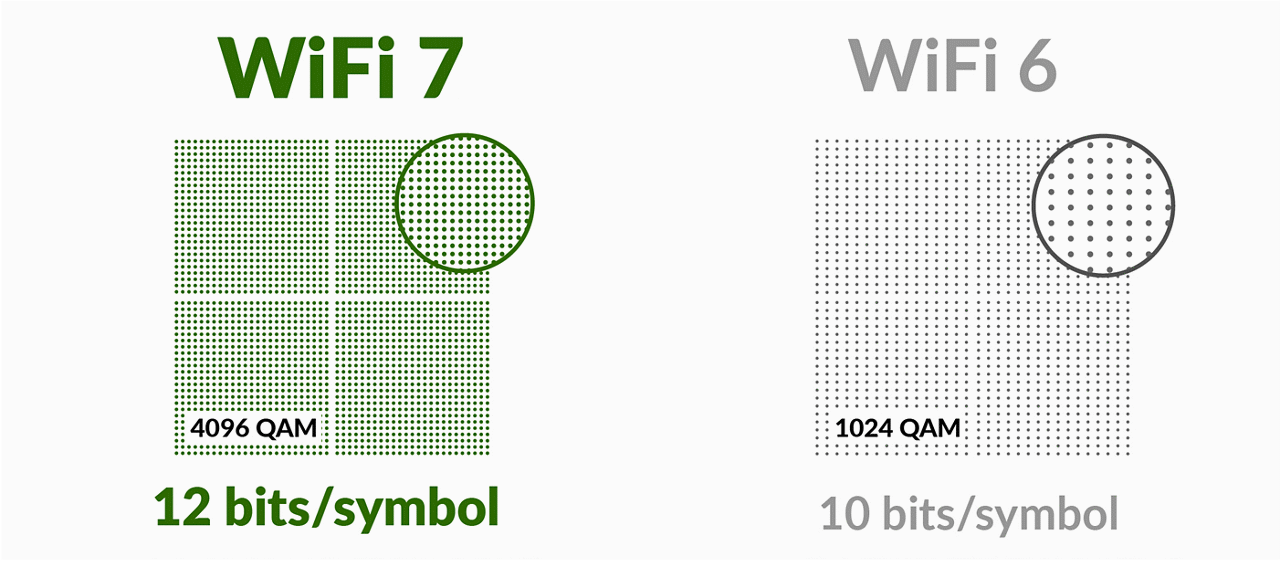
Figure 4. 4K QAM outpaces Wi-Fi 6 by 20%, setting a new standard for transmission efficiency.
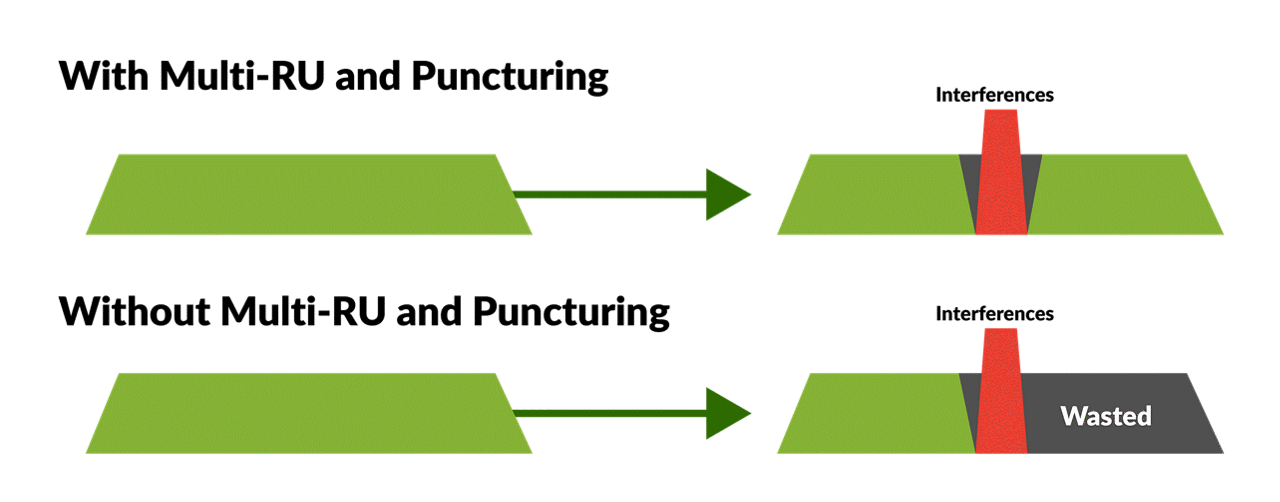
Figure 5. 512 CBAs streamline efficiency and cut overhead, marking a leap in network performance
Juniper Implementation
Juniper Networks simplifies the transition to Wi-Fi 7 with an AI-Native Networking approach, that delivers exceptional wireless experiences by streamlining operations, and optimizing, scale, agility, and security. Through close integration of new access points (APs) and high-power switches with Juniper Mist AI, Juniper can provide proactive network management that maximizes the benefits of Wi-Fi 7. The platform approach not only supports the high-throughput and low latency enabled by Wi-Fi 7 but it also allows for easy integration with the rest of the networking stack including SD-WAN, firewalling, location services, and network access control (NAC).
Juniper EX Switches, including the robust EX4400-48MXP and EX4400-48XP, are designed to meet the requirements of Wi-Fi 7 networks and are ideal for smart buildings and environments where sustainability is a priority. Delivering up to 3600W of Power over Ethernet (PoE), these switches are ideally suited for supporting the high power requirements of Wi-Fi 7 Access Points (APs) as well as other critical systems within smart buildings.
Finally, Wi-Fi the way it should be
Get the efficiency, resiliency, and visibility you need to deliver better network experiences. See why everyone's switching to Juniper Mist Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi 7 FAQs
What problems does Wi-Fi 7 address?
Wi-Fi 7 addresses the demands for denser, more efficient, and more capable wireless networks that are a part of the natural evolution of IT. It supports the ever-increasing need for higher data throughput and support for latency-sensitive applications like high-definition video streaming in high-density environments.
With its groundbreaking features, including 320 MHz super wide channels, Multi-Link Operation (MLO), 4K Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), and efficient spectrum resource scheduling, Wi-Fi 7 is engineered to revolutionize connectivity. These innovations not only promise multigigabit speeds but also aim to deliver unparalleled reliability and consistently superior user experiences.
What’s driving Wi-Fi 7 adoption?
Wi-Fi 7 adoption drivers are centered on technology's ever-changing needs for greater performance and lower latency. Wi-Fi 7 will enable the next generation of immersive experiences—from interactive classrooms, telemedicine (tele-diagnostics and tele-surgery), AR/VR applications to ultra-high-definition video streaming. It addresses the significant demand for higher data throughput and minimal latency in densely populated network environments. Groundbreaking enhancements like 320 MHz channels, Multi-Link Operation (MLO), and 4K QAM—each designed to support robust, efficient, and high-speed wireless connections—will fuel Wi-Fi 7 adoption.
What are the advantages of Wi-Fi 7 deployments?
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) is set to revolutionize wireless technology by delivering high-speed, high-density, and highly reliable connectivity. This new standard introduces several key advancements designed to meet the escalating demands of modern digital ecosystems. Key features and advantages include:
320 MHz Super Wide Channels:
- Enables remarkable data throughput, propelling device speeds into the multigigabit range.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO):
- Optimizes traffic balance to ensure sustained throughput and reliability.
4K QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation):
- Pushes data rates 20% beyond those of Wi-Fi 6.
512 Compressed Block Acknowledgment (BlockAck):
- Reduces overhead and enhances efficiency, particularly beneficial in dense network environments.
Wi-Fi 7's capabilities are more than just incremental improvements; they represent a significant leap in efficiency and performance. These advancements are designed to accommodate the network demands of both today and tomorrow. When combined with AI and automation that enable proactive troubleshooting and management, Wi-Fi 7 can provide unparalleled connectivity and operational efficiency, positioning enterprises for future success.
What are the key capabilities of Wi-Fi 7?
Featuring 320 MHz super wide channels and Multi-Link Operation (MLO), Wi-Fi 7 delivers transformative gains in throughput and efficiency, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive environments. Additionally, 4K QAM enhances data rate transmission by 20% over Wi-Fi 6's 1024 QAM. Advanced 512 Compressed Block Acknowledgment (BlockAck) optimizes network protocols by reducing overhead and boosting overall network efficiency.
Because Wi-Fi 7 introduces new tuning and management challenges, AI and automation will be key to maximizing Wi-Fi 7 performance while controlling costs.
What Wi-Fi 7 solutions/productions/technology does Juniper offer?
Juniper Networks is leading the way in Wi-Fi 7 technology, with a suite of products designed for the next-generation wireless standard. Our product lineup includes the new AP47 Series Access Points, engineered to deliver high-performance Wi-Fi 7 with integrated location services for demanding enterprise environments. The AP47 features advanced technology like a dedicated tri-band fourth radio, which functions as a network, location, and security sensor as well as a synthetic test client radio and spectrum monitor for improved client experience visibility in the Juniper Mist Cloud.
Wi-Fi 7 has increased power demands. The 3600W Juniper EX4400-48MXP and EX4400-48XP switches are designed to deliver industry-leading wired performance and seamlessly complement Wi-Fi 7 networks. These switches transform approaches to electrical systems in networking while helping control OpEx and supporting sustainability. Through their ability to deliver 3600W of PoE, they can handle the significant electrical loads and the multigigabit traffic of Wi-Fi 7 APs. They also work seamlessly with the Juniper AI-driven Campus Fabric and Juniper Mist Wired Assurance for Day 0, Day 1, and Day 2+ operations, ensuring efficient deployment, proactive monitoring, and ongoing optimization of the network.
With respect to security, Wi-Fi 7 also introduces a new set of challenges; more devices, bandwidth and capacity, and complexity mean more opportunities for attackers. Juniper Mist Access Assurance, an identity-based network access control (NAC), enforcing Zero-Trust policies and leveraging AI-Native insights, provides key capabilities for reducing the attack surface, simplifying operations, and strengthening security posture.
What is the difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7?
Wi-Fi 6, or 802.11ax, focuses on enhancing network efficiency and performance in dense environments. With features like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), Target Wake Time (TWT), and 1024-QAM, Wi-Fi 6 delivers up to 9.6 Gbps. It supports higher data transfer rates than previous generations, reduced latency, and improved battery life, laying the foundation for today’s smart ecosystems and complex applications.
Wi-Fi 7, or 802.11be, leapfrogs Wi-Fi 6 with 2x throughput. It introduces 320 MHz channels, Multi-Link Operation (MLO), and 4K-QAM, targeting data rates beyond 30 Gbps. Wi-Fi 7 leverages the 6 GHz band, offering greater reliability and reduced latency.
Should I upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 or 7?
Before adopting Wi-Fi 7, ensure that vendor products integrate seamlessly with your overall architecture to avoid short-lived investments. Historical issues with the early adoption of 802.11n and initial phases of Wi-Fi 5 underline the critical importance of interoperability.
Prioritize modernization: Traditional architectures, which are highly manual and network-centric, lack the scale, flexibility, and end-to-end visibility required to support today’s users and the IT departments that manage them. Moreover, while Wi-Fi 7 increases performance with 320 MHz channels, MLO and 4K QAM, it will also require more tuning and management, adding to the challenges. That’s why, before or during your transition to Wi-Fi 7, the most important steps to simplify operations and unlock efficiencies for your overburdened IT team are to:
- Update your legacy network
- Move to the cloud
- Harness AIOps capabilities
- Secure users and devices
Consider Wi-Fi 6E as an option for urgent near-term needs: For immediate needs, Wi-Fi 6E represents the most significant performance enhancement in the last decade, delivering 6 GHz spectrum benefits. It is a deployment-ready option for near-term upgrades, proofs of concept, and network planning. The Wi-Fi 6E infrastructure will also streamline your transition to Wi-Fi 7 when ready.
The Market Maturity Timeline: Remember that widespread Wi-Fi 7 adoption requires client devices and reliable interoperability. Enterprises should feel confident deploying Wi-Fi 6E now while preparing for Wi-Fi 7 rollout as the ecosystem evolves.






















