Delivering on the O-RAN Promise with RIC and SMO

In this keynote, Marc-Andre Bordeleau, Senior Director Product Management from Juniper. Networks highlights the progress made on RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and the learnings from the RIC field trials. He also elaborates on solving the complexity of orchestration, automation, and service assurance with SMO.
Explore our Open RAN solutions.
You’ll learn
Progress on RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and learnings from RIC field trials
Solving complexity of orchestration, automation, and service assurance with SMO
Who is this for?
Host
Experience More
Transcript
0:00 foreign
0:08 great to be here this morning especially
0:11 to follow the presentation of Richard
0:12 about the direct because our topics are
0:15 very aligned very related so okay I'm
0:18 director of product management at
0:19 Juniper Networks and I work in the CTO
0:22 office and I'm in charge of the uh the
0:25 the portfolio of uh for all run so
0:28 covering the rig the Smo and also the X
0:30 apps and our apps and as you'll see also
0:31 we have a very strong focus on network
0:33 slicing for delivering slas in this
0:36 context
0:37 so for this session we'll look at how
0:40 the Rick and the Smo are contributing to
0:42 the delivery of the oran promise a
0:45 promise that is about openness it's
0:47 about interoperability multi-vendor
0:49 environment but also about bringing in
0:51 Innovation into the run with the use of
0:54 applications which can be AIML based so
0:57 for this session what I'll do is I'll go
0:59 over the experience that we acquired
1:01 over the years actually I'll focus on a
1:03 few trials and pocs that we have
1:05 delivered and as you'll see we as
1:09 Juniper we have the Rick and the Smo but
1:11 we're not in the business of developing
1:13 r-u-d-u-n-cu so that means that our rig
1:16 is built from the ground up for being a
1:18 multi-vendor rick so we have to of
1:21 course interpret and work with multiple
1:23 vendors of applications of course we
1:26 develop our own as well but trying
1:28 different application of X apps and our
1:30 apps and also we have to work with
1:32 different vendors of network functions
1:35 so really using the rig as a multiple
1:37 multi-vendor platform to deliver the uh
1:39 the oran vision
1:41 so with this let's just start with a uh
1:45 just a quick overview of what we believe
1:48 are the key success factors for Oran to
1:51 be successful so of course at the
1:53 beginning and that's at the very core of
1:55 everything in Oran that's the O in o-run
1:57 or open run right openness so openness
2:00 it all starts with the specifications
2:02 right having the industry to contribute
2:04 and Define these standard the standard
2:07 architecture standard apis tip also to
2:10 provide let's say commercialization
2:12 proof point for validation and the
2:14 badges and of course the platform the
2:17 interfaces have to be standard and
2:19 compliant to those
2:21 but having the specs in itself alone is
2:24 not enough right we need the whole
2:25 ecosystem to adhere to these specs to
2:27 implement these standards and to really
2:30 work as an industry to interpret and
2:32 have multi-vendor integration
2:35 so openness you'll see that throughout
2:37 the presentation is really a strong
2:39 foundation for everything we do and
2:41 everything that needs to be done in our
2:42 run
2:43 so next of course we strongly believe in
2:46 the value of Automation and control in
2:49 Oran right this is being brought into
2:51 the architecture of Oran with the Rick
2:53 the random surgeon controller and the
2:55 Smo the service management and
2:57 orchestration platform so we'll talk at
2:59 lent about these two key component
3:00 components of Oran during this talk and
3:03 last but not least the real value of
3:05 Oran comes when we have these two
3:07 pillars right then we can start talking
3:09 about bringing Innovation there's really
3:12 Innovative use case no run and these use
3:15 case indeed can be categorized under
3:16 different buckets right there are capex
3:18 and OPEC savings use cases like the Suns
3:21 Energy savings QE Qs optimization use
3:24 case and of course there are a bunch of
3:26 use cases that bring a new business
3:29 model and New monetization Opportunities
3:31 and of course Network slicing is at the
3:34 very core of that in the 5G setting
3:36 so these are some key Foundation that
3:39 we'll be talking during this this
3:40 presentation
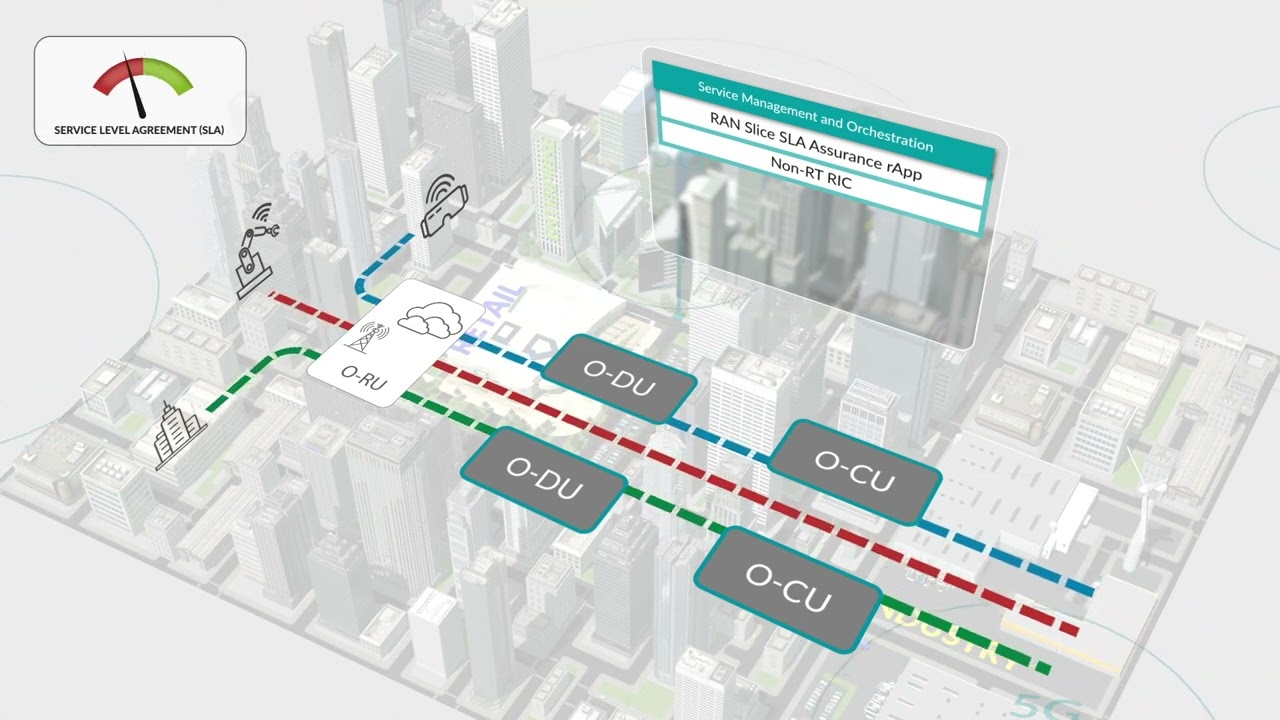
3:41 so and before talking about the uh the
3:44 actual trial and the experience we'll
3:46 learn I'll just like to take a few
3:47 minutes to review the oran architecture
3:49 it's a very simplified architecture here
3:51 and I like the key components that we'll
3:53 be talking about
3:54 so of course at the bottom of this
3:56 there's the of course the the ram
3:58 Network functions the ru the DU and the
4:00 CU and these functions can be either
4:03 physical Network functions PNF
4:05 or Cloud native or virtualize as CNF or
4:08 vnf in that case they run in the ocloud
4:11 infrastructure defined by Oran that's
4:13 really a distributed Cloud environment
4:15 that can become well coming from
4:17 multiple providers and contains tens of
4:19 thousands of cell sites Edge Cloud
4:21 Regional cloud and so on so it's highly
4:24 distributed desegregated infrastructure
4:26 and also of course the network functions
4:28 as well
4:29 then on top of that and that's going to
4:32 be mostly the topic of the discussion
4:33 comes the wreck in the center the rank
4:36 the rig as you know has two flavors
4:38 right so there's the non-real time Rick
4:40 and the near real time rig they both run
4:42 applications our apps on the
4:44 non-real-time rig and accepts on the
4:46 neural time rate they have different
4:48 role and responsibilities into the
4:49 orange architecture also their control
4:51 Loop is different right the near real
4:53 time rig is normally deployed closer to
4:56 the DUS and CU for having a faster
4:58 control Loop uh the near real-time rig
5:01 provides control to the network
5:03 functions whereas the not the
5:04 non-real-time rig has a much broader
5:07 scope of visibility to accumulate data
5:09 from the entire network and then instead
5:12 of providing near real-time control it
5:15 provides a policy guidance to the
5:17 various near real-time rigs that are
5:19 deployed in the entire networks and
5:20 again the applications they can come in
5:23 pair of our apps and X app depending on
5:25 their level of operation and how they
5:27 are deployed on the rigs so we'll talk
5:29 Atlanta about the rig and we'll talk
5:31 also about the Smo which is represented
5:34 with the the big rectangle over here so
5:36 the Smo is composed of multiple
5:38 functional block so this is a Nomine a
5:41 software architecture but this is just
5:42 representing the functional block so at
5:46 the very left of this diagram here is
5:48 the what Oran called the focon that
5:51 stands for Federated o cloud
5:53 orchestration and management that's
5:56 basically the ability to manage the life
5:58 cycle of the infrastructure so the
6:00 ocloud so bring let's say bootstrapping
6:03 from zero touch provisioning new o cloud
6:05 or new cell sites right managing life
6:08 cycle of these clouds scaling it and
6:10 scaling out managing defaults so the
6:13 whole life cycle of the O Cloud
6:14 infrastructure is provided by the focus
6:16 component
6:18 so that's one the nfo next that stands
6:21 for Network function orchestrator that
6:23 can be similar to the hcnf video right
6:26 whereas in the oran the nfo is not
6:29 necessarily restrained to an Etsy
6:30 environment so it can run also Cloud
6:32 native let's say infrastructure with
6:35 kubernetes so the nfo is responsible for
6:38 deploying the workload so the
6:39 containerize virtualized workload you
6:42 see the the the vdu or the uh the the
6:44 cus can be deployed through the nfo as a
6:47 network function orchestrator for Oran
6:50 then we talked about the rig and then
6:52 last but not least the run and ssmf is
6:55 defined by 3gpp but it is also embedded
6:58 into the oran architecture that is the
7:00 Run slice subnet management function
7:02 that's really the ability to manage the
7:04 f-caps the provision and the
7:06 provisioning of the slice of the Rand
7:09 slices if you like so basically creating
7:11 sizes managing their fault their
7:13 performance their configuration and then
7:15 once they are up and running the rig and
7:18 the X apps are app can take uh can take
7:21 control over these slides to ensure that
7:22 the SLE of the slicers are restricted at
7:24 all times so these are the main
7:26 components that we'll be talking and
7:27 we'll look at some trials and pocs that
7:30 we have delivered using these components
7:34 so starting with the rig so there are
7:37 I'd like to talk about four different uh
7:40 use cases that have been trialed
7:42 recently there are more than this but
7:44 highlighting these four so first
7:45 category and I'll dive into this is
7:47 about admission control
7:49 next one is about traffic steering third
7:52 is energy saving and last but not least
7:55 the Run slice slas runs
7:57 so starting with admission control so
8:01 this is a use case that runs as an
8:05 except and an R app that will trial and
8:07 demonstrated at various various
8:09 occasions and are in particular I'd like
8:12 to highlight two different uh trials
8:14 that we've run with this and in this
8:16 case the uh the partners also are public
8:18 so I can name the partners that were
8:19 engaged with us
8:20 so the first one the first mention I
8:22 would like to make is we've run a trial
8:25 at Vodafone
8:27 on their commercial Network in Turkey so
8:29 it was a real field trial with the rig
8:31 and the admission control application
8:33 in this case the Run vendor was parallel
8:36 Wireless and the accept our app was
8:38 developed by Juniper so so that that was
8:42 completed uh this year well sorry n of
8:44 22 and the other uh mention that I'd
8:47 like to make here the operator is not
8:49 public so it's a tier one operator but
8:52 the the demonstration was made on a it's
8:55 a it was a lab trial in that case was
8:58 made on a 5G network with network
9:00 slicing enabled so in that case we
9:02 called it slice aware admission control
9:04 because dsla the admission controlled
9:07 requirement they came from the slice
9:09 slice definition so really we
9:12 orchestrated the slice with the random
9:13 ssmf that you saw earlier we provided
9:16 the the SLE of the slides through the
9:18 gsma GST parameter and then this was
9:21 propagated to the rig and the rip in
9:23 real time ensured the uh the the respect
9:26 well the admission control and enforced
9:29 and Mission Control policies in this
9:31 case the Run vendor was Kaza systems
9:33 so how it works now so admission control
9:36 is really about when a network is under
9:40 provision meaning that there's not
9:42 enough resource to serve all the
9:44 admission requests by the US by the end
9:46 users right so in this case the network
9:49 has to make decision as to who is
9:50 admitted on the network as who is
9:52 rejected ggbp defines some mechanism
9:55 with the 5G core or the EPC to do
9:57 admission control but with the run and
9:59 the rig it brings additional
10:00 capabilities where you have visible
10:02 theme to The Specific cells and then you
10:04 can start doing some intelligent
10:06 balancing of the admission requests
10:08 across the cell so if a cell is let's
10:11 say a slice as an example as an SLA of
10:14 thousand uh admitted ues on the slice
10:19 right so if all the cells are used at
10:23 the same level so there's no problem you
10:24 can do a fair sharing of the admission
10:26 but what if let's say during a rush hour
10:29 right so in the downtown there's a lot
10:31 of visualization but at the neighborhood
10:32 there's no utilization request so with
10:35 the rig the admission control accepts
10:37 and our apps you can realize the
10:38 utilization on a per cell basis and then
10:41 change the admission policies on the per
10:44 cell to admit more users or less user
10:46 depending on the sale and you can do
10:47 that also across slices depending on the
10:50 slas the priority of the slices
10:53 so that's one use case that we have
10:55 trialled again in this case in two
10:57 settings but we've demonstrated that
10:59 many more times but that these were two
11:01 important one to uh to discuss so it
11:03 enables Priority Access to the network
11:04 for any user at any time based on
11:07 policies and configuration
11:11 next one is traffic steering so traffic
11:14 steering is a use case that was
11:16 co-developed with a partner parallel
11:18 Wireless they have actually developed
11:20 the X app they were providing the
11:22 network functions and Juniper we have
11:24 developed the r app to drive the
11:26 policies for that exam so this again was
11:28 demonstrated not demonstrated but trial
11:31 at Vodafone on their live Network in
11:34 Turkey
11:35 in the same trial as the admission
11:37 control that we saw so traffic steering
11:40 here is about
11:41 optimizing the network utilization of
11:43 the network resource so the rip is
11:45 looking at all time at the or the X apps
11:48 our apps are looking at visualization of
11:49 the cells across the network and if a
11:52 cell become congested at some point then
11:55 the application can make decision as to
11:58 well first of all look at the ues the
11:59 users which one are suffering from this
12:01 congestion are having low throughput
12:04 effectively and then decide on whether
12:06 it's possible to steer these user attach
12:09 them to other sales or end them over to
12:12 other base stations so that's the the uh
12:15 the the use case of traffic steering so
12:17 where you see in this case this uh this
12:19 user is attached to that cell but then
12:21 it's congested so the rig and
12:23 application will will make the decision
12:24 to offload to this cell here to remove
12:27 control so it has two benefits it
12:29 reduces congestion of the cell and it
12:31 also improves the user experience
12:33 because it gets additional throughput
12:35 and that's what we've seen in this trial
12:37 on the commercial networks on average
12:39 for cells that were congested when doing
12:42 traffic steering like this it was
12:44 possible to get to 15 30 average
12:47 throughput increase across the cell and
12:49 for those users that were severely
12:52 impacted by congestion that were steered
12:55 to other cells then we reach up to 40 of
12:57 throughput improvement
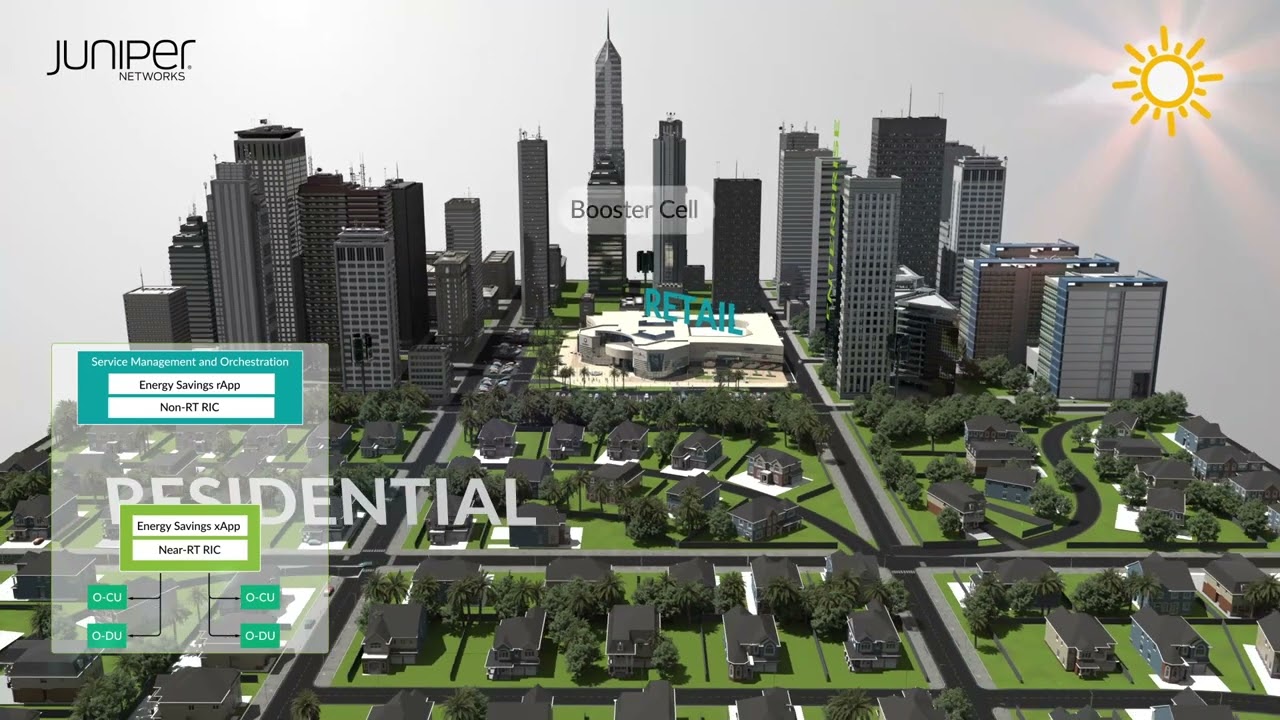
13:01 so next is a very important topic about
13:04 Energy savings right so that's another
13:06 use case that runs on the rip that we
13:09 have demonstrated in different
13:11 opportunities so one of those was in a
13:14 Oran plug Fest so in this case it was
13:18 running the application the Energy
13:19 savings applications from juniper and we
13:21 were partnering with keysights for the
13:25 simulation of the the platform they are
13:27 used the use and see so that one that
13:29 was that was realized in a plug Fest at
13:32 Oran
13:33 another opportunity where we
13:35 demonstrated this is at mwc We announced
13:39 a collaboration with era Technologies a
13:41 startup in AI that develops AI ml based
13:44 application and in this case era is
13:47 developed in our app it was only the RF
13:49 in this case not the X app but the r app
13:51 was controlling through the o1 mechanism
13:54 the uh the the Energy savings
13:57 of the run network in this case it was
13:59 simulated uh with the the network
14:02 function simulators of Viv
14:05 so again we integrated with another
14:07 vendor of network function or simulator
14:09 in that case
14:10 and in this simulation we observed up to
14:13 20 of Energy savings with this use case
14:18 and
14:20 and then last one I want to mention here
14:22 is about run slice SLA surround so as we
14:25 discussed at land in this session right
14:27 ensuring the SLA is a great way it's a
14:29 great new opportunity in 5G to deliver
14:31 services that are tailored for the use
14:34 the needs of the users and how to ensure
14:36 the SLA is respected at all time and so
14:39 on so through the Run slicing management
14:41 function we can provision the slices the
14:44 slices can be created so the day Zero
14:46 the day one uh provisioning and
14:49 operation of the slice the f-caps but
14:51 now when it comes time to optimize the
14:55 slice to make sure they respect their
14:56 SLA at all times so what if the
14:58 throughput requirements are not met the
15:00 SLA record the latency requirements are
15:02 not met then the Run slice SLA s runs
15:05 can come into play to make decision in
15:07 their prioritization or changing
15:09 configuration or control over the A1 E2
15:12 channel of the rig so this is another uh
15:16 use case that we have demonstrated in
15:19 plug Fest again with keysight the
15:21 application in this case is coming from
15:23 juniper and Juniper is investing a lot
15:25 in slicing either slicing management and
15:27 slicing SLA Assurance we have a lot of
15:30 patents in this area and also a lot of
15:31 contribution we're driving for example
15:33 at Oran in the working group one the
15:35 slicing activities and we're deeply
15:37 engaging to many working groups related
15:39 to slicing from one two three six and
15:42 nine as well
15:47 so okay I String the SLA of the slice so
15:50 these are four use cases that I wanted
15:51 to highlight here of course the goal and
15:54 the uh the ambition is to create just
15:56 like a an app store for mobile phones
15:59 right you want to welcome as many vendor
16:01 of applications to develop on our rig
16:05 and have the broadest possible portfolio
16:07 and for this we are and we're offering
16:09 to the vendors and SDK to develop
16:11 application and open apis so Oran is
16:14 defining the apis the Rick API on the
16:16 near real time rig and the uh
16:19 R1 API on the non-real-time rig for
16:22 applications develop on Direct
16:24 so we're definitely contributing to
16:26 these the specification the
16:28 specification at all run are not
16:30 completed yet so they're in stage one so
16:31 the uh well it's the the general
16:33 principles have been defined but the
16:35 stage 3 specifications are not completed
16:38 so the way we approach that is of course
16:40 we're contributing at Oran we're deeply
16:42 engaging to the specifications but we're
16:44 not waiting for Oran in the sense that
16:46 we have implemented pre-spec R1 and rig
16:48 apis and of course contributing into the
16:52 spec and then we will be complying with
16:54 the spec as the Evolve if they deviate
16:56 from what we believe they will be
16:58 achieving
16:59 so the uh the key learnings from this
17:03 right so first of all all these trials
17:06 and these pocs they are confirming that
17:09 the Rick is an open and interpretable
17:11 platform so this is we this is something
17:14 that we do that we work on on the daily
17:15 basis it's extremely important to comply
17:17 and to follow the specifications
17:19 participate in plug Fest in order to to
17:22 make sure there is compliance and
17:23 Enterprise
17:25 we have seen over times who have been
17:27 developing the rig for actually uh many
17:30 years even before I mean we even before
17:33 Oran was forming the x-run days there
17:36 was a some controller that was developed
17:37 and then this has evolved over time uh
17:40 so we've seen that there is with sdks
17:42 apis the development times for
17:44 third-party developers has really
17:46 accelerated so they're still uh
17:48 Improvement to be made there to even
17:50 further improve the API CSD case but
17:53 we've seen that in some cases for simple
17:55 application the the whole porting of the
17:57 application can take just a few days of
18:00 course more complex application will
18:01 take longer but still it has really
18:04 accelerated that's one of the the thing
18:06 we've seen over the year uh with the rig
18:08 another thing also is the integration
18:10 with the CU and the EU vendors of course
18:13 if these vendors are o-round compliant
18:16 supporting the E2 interface then it's a
18:18 matter of running the inter probability
18:20 testing and it works quite well now if
18:22 the vendor are not or uncompliant so
18:25 we've also run a trial at a tier one
18:28 operator where we add to integrate with
18:30 a uh a non-2gbp Oran compliant vendor
18:34 and for this of course for the near real
18:36 time rig if there's no E2 there's no E2
18:38 but for the non-real-time rate to the
18:40 f-caps configuration channel the 01 or
18:43 3gb mechanism then it's possible to
18:45 configure and let's say get performance
18:49 metrics and operate on that
18:51 so a lot of learnings there as well
18:54 on the real-time management of the ratio
18:56 resources that's a very important topic
18:59 of course there's a lot of improvement
19:00 to be made there of course the Run
19:02 vendor supporting the E2 service model
19:05 is key to enable all the benefits of
19:08 Oran but what we've seen is that it is
19:10 possible uh when the vendors they open
19:13 up the 2sms to do that we've done that
19:15 with the admission control and with the
19:17 traffic traffic steering uh well also
19:20 csun's applications and so on
19:23 and last but not least we definitely see
19:26 that the ecosystem is maturing it's not
19:29 I mean we're not fully there yet but
19:31 really the whole run we see a lot of
19:33 contribution at Oran we see many
19:36 companies contributing the specs are
19:37 maturing are evolving the whole uh the
19:40 the whole operator the the operator
19:42 industry from what we see from our
19:44 vendor point of view is really a huge
19:47 interest from operator so a lot of
19:49 requests excellent questions from the
19:51 operator willingness and trialing and
19:53 trying the rig so really the it's not
19:55 like uh us lenders that are trying to
19:58 convince operator that this is important
19:59 that's the other way around right so the
20:01 oran is is at the foundation from
20:03 operator so the rip I mean your
20:05 presentation was very clear right that
20:06 the Rick is a key Cornerstone of that
20:09 and then Innovative partnership are
20:11 being formed and of course there's more
20:13 and more applications that are being
20:14 available
20:17 okay so now let's talk quickly uh about
20:20 the uh the the Smo so uh the Smo again
20:24 is the whole management of the run
20:26 network
20:27 uh there are I mean the the whole Telco
20:31 infrastructure is evolving we all know
20:33 that right there are different
20:35 challenges and uh it's complex to manage
20:38 this environment but let's say these
20:39 let's review these uh these key Concepts
20:42 like the foundations for the SML so of
20:44 course the Telco infrastructure is
20:46 evolving right with cloudification with
20:48 the disaggregation software Define
20:49 everything right so this is a whole new
20:53 concept if we compare two years ago so
20:55 these new technologies have been have to
20:58 be taken into account when we do service
21:00 orchestration and management of the
21:02 Telco Network
21:03 of course networks are extremely massive
21:07 complex and this is not getting any
21:09 easier with the identification in 5G so
21:13 Smo have to operate at massive scale so
21:15 there's no way this can be done let's
21:17 say manually it has to become
21:19 intelligent
21:20 and then last but not least again is the
21:23 need for on-demand service services on
21:26 these teleco networks so how do we
21:28 monetize this in this investment how do
21:31 we uh also offer differentiated service
21:34 to the customers to fit their needs
21:37 right whether this is private mobile
21:38 networks that can be created with slices
21:41 on top of the public network or can be
21:44 for deploying an mvno on top of the
21:47 network or any industrial or vertical
21:50 use cases as we can see on this slide
21:52 here so each of them have their
21:53 different requirements their different
21:55 slas so being able to orchestrate and
21:58 manage these services on top of a
22:02 extremely massive and complex
22:03 environment and with the new
22:06 technologies that we see as all the
22:07 challenges that the SML have to address
22:12 so
22:13 again just to oh there's a display
22:15 problem here but the uh just to
22:17 summarize the Smo is containing these uh
22:21 these functions here so the focom the
22:23 nfo the non-real-time rig and the Rand
22:25 and ssmf and it collaborates of course
22:27 with the near real-time rig for the
22:28 control of the network functions and one
22:31 trial that I'd like to mention here is
22:34 we were asked by a uh well a tier one
22:37 operator to demonstrate and prove how
22:40 that it is possible to realize 5G
22:42 Network slicing in a multi-vendor
22:45 environment so really that was the key
22:47 requirement of that trial was to go into
22:50 multi-vendor so there were Juniper of
22:53 course was providing the ran Smo and the
22:55 rig in that case the network functions
22:58 were provided by another vendor core
23:01 domain management well also another
23:02 vendor and the at the top level the
23:04 service orchestration was provided by
23:07 another vendor so it was truly
23:09 multi-vendor in that case
23:11 so in this trial of course we we learned
23:14 a lot right it's possible with the 3gbp
23:17 specs the all run specs to realize
23:19 slicing what we've done here is to do
23:21 the day Zero and the day one operation
23:24 of the slice of the provisioning and
23:25 being able to create two slices with
23:27 sharing of component and SL enforcement
23:30 with the admission control and the SLA
23:33 exceptionara
23:35 so integration at the beginning of
23:38 course we not everybody was adhering to
23:41 the 3db specifications and or run
23:43 specification but in the end we we
23:45 address the concern and we were able to
23:48 succeed in this POC so that's uh
23:52 that's it so the basically conclusion
23:54 really the takeaway of that presentation
23:55 is that we need to continue shaping and
23:58 contributing to Oran to GBP and the
24:00 various standard organization this is
24:02 really important embracing the open and
24:04 Center their architecture apis and
24:06 making the Radio Data available for the
24:07 industry to evolve and have the
24:09 application developer to be able to come
24:11 up with very Innovative applications
24:13 fantastic thank you very much put your
24:15 hands together
24:17 [Applause]
24:18 thank you that's brilliant
24:20 um yeah just one quick question maybe
24:22 before we get to break well
24:24 okay thank you okay very quick questions
24:29 um first off first and in the near time
24:32 and the now real time rig what language
24:35 do you use to develop the algorithms
24:38 inside the different to develop these
24:40 sorry the application what language do
24:43 you use like Pi sound or r or whatever
24:45 the language is normally uh Juniper use
24:48 that that we okay so our wreck is I mean
24:51 first of all it's built on the ground up
24:52 from the ground up with Cloud native
24:54 principles so it runs kubernetes
24:56 applications so it's a mix of go
25:00 language implementation and C plus plus
25:02 so that's the rig and the application
25:03 then they can be completely independent
25:05 we have open apis and SDK so application
25:07 can be completely different but these
25:09 are languages can you steer leverage all
25:11 the API interface of course let's say it
25:14 doesn't matter if I use Pi sound or r or
25:17 Matlab for or the algorithm application
25:20 part right yes no application yeah the
25:23 open API is well defined also we have
25:26 SDK SDK we have some Hello World
25:29 application to show you how to use it
25:31 operated and yeah that makes sense can
25:34 you please go to the SL mode slide and
25:37 yeah over here so
25:40 um you address the NSS MF yeah ran and
25:43 also for the uh 5gc and ssmf actually
25:46 and in that in there no spawn there are
25:49 two different network entities like nsmf
25:53 and the csmf are you going to place it
25:57 as a part of Smo in the future or you
26:00 you take it out of the scope of the SML
26:04 over here and in our experience we we
26:07 developed these two Network entities for
26:09 China mobile and China Unicom but these
26:13 two Network entities and are now part of
26:16 the 5G OSS system I'm just asking if you
26:19 have some road map where are you going
26:22 to place these two Network entities in
26:25 the future for oksmo so we can I mean I
26:28 can give a
26:30 eye level uh response to this and we can
26:33 definitely talk about rulemap in details
26:35 separately but really so the definitely
26:38 here what I'm showing is Oran Smo so
26:41 it's in this trial we were asked to
26:43 provide this part the Run Part but
26:46 you're absolutely right right 3gbp
26:48 defines csmf for the Communication
26:50 Service management function the nsmf or
26:52 network slice management function for
26:54 end-to-end slicing management and then
26:56 in each of the domains right around the
26:58 core transport is ITF but the random
27:00 core there's the an ssmf for size subnet
27:03 so indeed the vision is to realize
27:06 end-to-end slicing that's really
27:07 important so for this trial we provided
27:09 the ran Smo but in our view right
27:12 there's a notion of multi-domain Smo
27:15 that contains indeed csmf and SMF
27:19 that has the core and ssmf and the TN
27:23 call it nssm if you want it's it's ietf
27:26 it's a bit different but the interfaces
27:28 are being defined
27:30 and what is important though is that
27:32 these components they all use standard
27:35 API so we see really 3gbp TM Forum right
27:38 there's various iitf apis that are being
27:40 defined so adhering to these apis is
27:42 really important and that's what we
27:44 demonstrated in this POC so that you can
27:46 mix and match the components but yeah
27:48 that's that's a great question
27:51 fantastic thank you very much I think
27:53 that's all we've got time for it's now
27:54 the uh the coffee and networking break
27:57 after we'll be joined by uh Simona from
28:00 Bell to talk dive more into automation
28:04 as well but thank you for thank you
28:06 [Applause]
28:09 thank you