What is 400G?
What is 400G?
400G is the next generation of cloud infrastructure. With a fourfold increase in maximum data transfer speed over 100G, 400G addresses the massive bandwidth demands being placed on network infrastructure providers. Open systems, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud storage all contribute to exponential traffic growth. As large data centers transition to faster, more scalable infrastructures, high-capacity connectivity is essential to keep pace with the ever-expanding number of users, devices, and applications.
To fully understand what’s driving the need for 400G, it’s important to distinguish the various ways 400G can be defined and used in data center networking conversations.
- 400G most commonly refers to a solution that offers 400G of capacity on one 400G wavelength. It’s interchangeable with 400GbE and 400Gb/s depending on the context.
- 400GbE refers to the next capacity rate in Ethernet interfaces that can travel through a single link. It’s based on the approved IEEE 802.3bs standard that 400GbE physical layers, management parameters, and Media Access Control (MAC) parameters must meet.
- 400Gb/s refers to the speed at which data is transferred. In this case, 400 billion bits of information travel through a single optical wavelength every second.
What Problems Does 400G Solve?
Traffic demands will continue to push data center servers to their capacity limits. 400G-capable solutions are ideal for high-volume telco providers, large data centers, and enterprises grappling with unrelenting traffic growth. In addition, 400G promises the power, efficiency, and density required for 5G and emerging applications such as augmented and virtual reality and 4k video streaming.
The IEEE 400GbE standard achieves data transfer speeds that are 4x faster than 100Gb/s and provides far greater efficiency as larger pipes are easier to manage and transmit bits at a lower power percentage. A single 400G port on a router, along with optics, will cost less than four individual ports of 100G (4 x 100G) with their own set of 100G optics. And the same is true for power: A single 400G port consumes less power than the aggregate power consumed by four individual 100G ports.
Additionally, 400Gb/s speeds allow for scale-up and scale-out architectures optimized for enhanced resilience and reduced blast radius.
Emerging 400G equipment, such as optical transport products, compact connectors, high-speed optical transceivers, and fiber management, supports 400GbE scale-up and scale-out networks with significantly low cost-per-bit, high density, and reliable throughput.
How Does 400G Work?
400GbE technology requires the ability to process more symbols per second and advanced modulation formats to support more bits per symbol. Combined, these abilities enable the transport capacity of 400Gb/s per wavelength to be delivered at the optimum cost per bit with a smaller form factor, fewer points of failure and interfaces, and lower power and heating—all with 4x the capacity of 100Gb/s.
What is 400G?
400G is the next generation of cloud infrastructure. With a fourfold increase in maximum data transfer speed over 100G, 400G addresses the massive bandwidth demands being placed on network infrastructure providers. Open systems, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud storage all contribute to exponential traffic growth. As large data centers transition to faster, more scalable infrastructures, high-capacity connectivity is essential to keep pace with the ever-expanding number of users, devices, and applications.
To fully understand what’s driving the need for 400G, it’s important to distinguish the various ways 400G can be defined and used in data center networking conversations.
- 400G most commonly refers to a solution that offers 400G of capacity on one 400G wavelength. It’s interchangeable with 400GbE and 400Gb/s depending on the context.
- 400GbE refers to the next capacity rate in Ethernet interfaces that can travel through a single link. It’s based on the approved IEEE 802.3bs standard that 400GbE physical layers, management parameters, and Media Access Control (MAC) parameters must meet.
- 400Gb/s refers to the speed at which data is transferred. In this case, 400 billion bits of information travel through a single optical wavelength every second.
What Problems Does 400G Solve?
Traffic demands will continue to push data center servers to their capacity limits. 400G-capable solutions are ideal for high-volume telco providers, large data centers, and enterprises grappling with unrelenting traffic growth. In addition, 400G promises the power, efficiency, and density required for 5G and emerging applications such as augmented and virtual reality and 4k video streaming.
The IEEE 400GbE standard achieves data transfer speeds that are 4x faster than 100Gb/s and provides far greater efficiency as larger pipes are easier to manage and transmit bits at a lower power percentage. A single 400G port on a router, along with optics, will cost less than four individual ports of 100G (4 x 100G) with their own set of 100G optics. And the same is true for power: A single 400G port consumes less power than the aggregate power consumed by four individual 100G ports.
Additionally, 400Gb/s speeds allow for scale-up and scale-out architectures optimized for enhanced resilience and reduced blast radius.
Emerging 400G equipment, such as optical transport products, compact connectors, high-speed optical transceivers, and fiber management, supports 400GbE scale-up and scale-out networks with significantly low cost-per-bit, high density, and reliable throughput.
How Does 400G Work?
400GbE technology requires the ability to process more symbols per second and advanced modulation formats to support more bits per symbol. Combined, these abilities enable the transport capacity of 400Gb/s per wavelength to be delivered at the optimum cost per bit with a smaller form factor, fewer points of failure and interfaces, and lower power and heating—all with 4x the capacity of 100Gb/s.
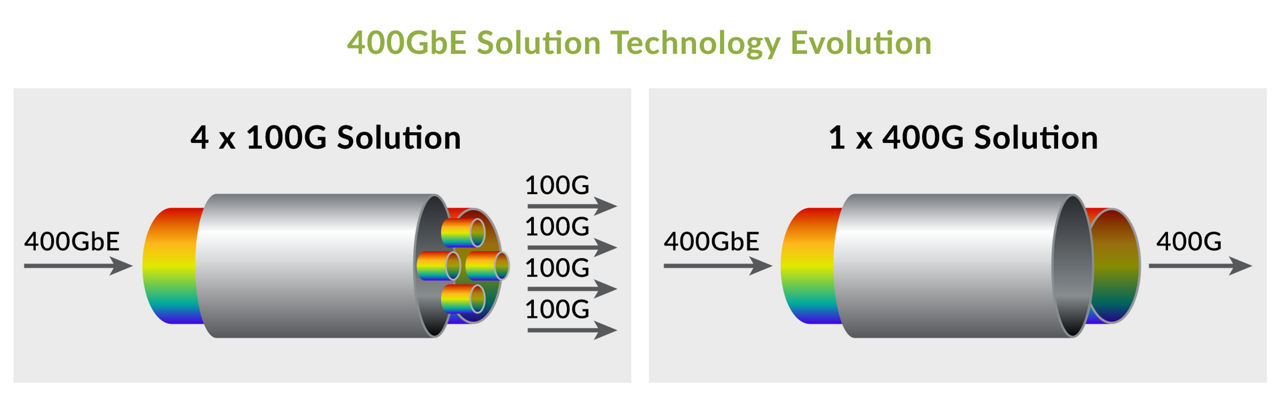
The evolution of 4 x 100GbE to 1 x 400GbE has brought significant reductions in energy and footprint.
Juniper 400G Solutions
Today’s network infrastructures require built-in scalability, flexibility, simplicity, and security. Network operators need to support burgeoning bandwidth demands now and in the future, reliably and cost efficiently.
With higher throughput, power and space savings, and interconnect options, Juniper’s 400G solutions are designed to help network operators achieve these goals as they continue to innovate in the cloud era.
400G FAQs
What is 400G technology?
400G represents the next generation of optical transceivers. With a four-fold increase in maximum data transfer speed over 100G, 400G addresses the massive bandwidth demands being placed on network infrastructure providers.
What’s driving 400G adoption?
Massive growth in cloud computing, AI, and 5G have driven an exponential demand for high-bandwidth, scalable solutions that can support new 400G techniques and architectures. The need for improved operational workflows, better economics, and concrete business outcomes continues to push 400G adoption forward.
Who is looking to implement 400G?
400G-capable solutions are ideal for high-volume telco providers, large data centers, and enterprises grappling with unrelenting traffic growth. Hyperscale data center operators were the first to embrace and deploy 400G solutions, which are now being adopted by a broader group of forward-looking and innovative operators facing similar high-traffic challenges.
What are the advantages of 400G deployments?
400G enables a new level of scale. Providing 4x higher bandwidth per RU than 100G, 400G optical transceiver modules deliver a lower cost per bit by delivering the same bandwidth in less physical space. 400G pipes are also easier to manage with fewer overall ports, and silicon advancements reduce watts consumed per gigabit, allowing for the transmission of more bits at a lower power.
What 400G solutions does Juniper offer?
Juniper offers a complete portfolio of 400G-capable modular and fixed chassis switches and routers for both WANs and data center networks. These solutions span the PTX Series Packet Transport Routers, MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platforms, and QFX Series Switches. They’re all optimized for scale-up and scale-out use cases, including core, peering, data center edge, data center interconnect (DCI), and multiservice edge applications.






















